

1992 R


![]()
MIKKEL AALAND and RUDOLPH BURDGER / DIGITAL PHOTOGRAPHY - 1992. Mikkel
Aaland is an award-winning American photographer and is known for work
in the early days of digital photography. His documentary
photographs have been exhibited in major institutions around the world,
including the Bibliotheque Nationale in Paris and the
former Lenin Museum in Prague. Aaland is the author of
books featuring his own photojournalism as well as works on digital
imaging and various Adobe Photoshop products.
Rudolph Burger received his
undergraduate degree from Yale University, a graduate degree from Yale
University, and a doctorate degree from the University of
Cambridge. He is a specialist in color calibration
technology. Dr. Burger is Chief Executive Officer at Scipher Plc
and Managing Partner at Woodside Capital Partners LLC. He is on
the Board of Directors at Seeing Machines Ltd. and Bango Plc.
Digital Photography, Random House,
New York, 1992, was an early book which described the equipment and
techniques of digital photography and image manipulation. It was
written especially for professional and amateur photographers and
graphic designers who wished to exploit the then new field of
digital imaging. The book discusses both still video and the few
digital cameras available at that time. This book is important to
collectors of early still video and digital cameras because it provides
much useful information about those early electronic cameras and
associated equipment.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mikkel_Aaland
Canon EOS Rebel II SLR (EOS 1000 N in Europe, EOS 1000 S in Japan) - 1992. First Rebel upgrade. The Rebel II is without built in flash. The model with flash is the Rebel S II. EF lens mount. Shutter 30 Sec. to 1/2000th plus bulb. The EOS Rebel II usually came with a 35-80mm f/4-5.6 zoom lens. This camera in excellent condition with the original 35-80mm lens, 80-200mm lens, Promaster 1.7 teleconverter and 200E flash unit was donated by our good friend Chuck Haines.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GsHCUI0TItE



![]()
CANON
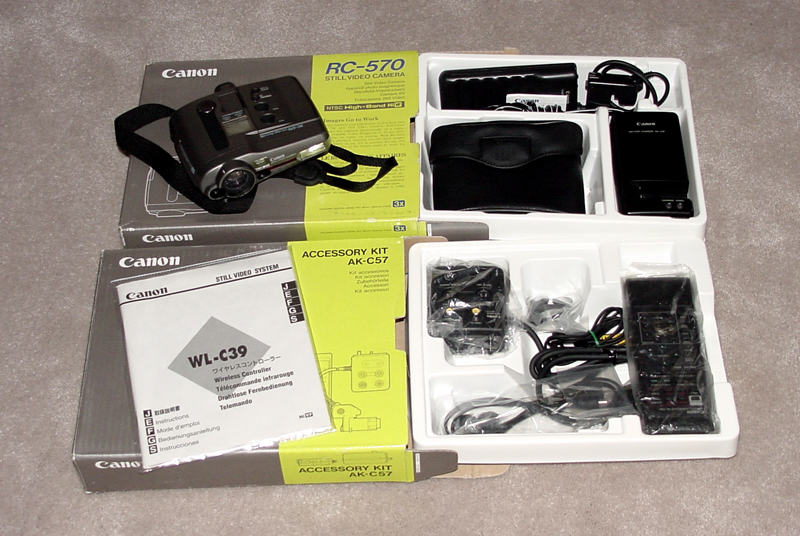
RC-560/570 - 1992. The RC-560/570
still
video camera used a 1/2 inch, 410,000 pixel CCD image sensor and
Hi-band
specification to produce images with horizontal resolution of 450 TV
lines.
3X zoom and integral automatic flash. An optional recording
interface
daughterboard for the Mac NuBus card could give the additional
flexibility
of converting digital images to analog and recording them with the
camera.
This would allow downloading a computer-generated presentation onto a
video
floppy from Aldus Persuasion or similar package (including photos
originally
taken by the electronic camera), as a series of video slides.
When
transferred into the computer, the pictures were digitized into 24-bit
color or 8-bit grayscale tiff or pict files. The Canon RC-570
sold
for $3,400. The Mac kit (RC-560) with NuBus digitizer board was $4,100 including
the camera. Adding the digital-to-analog output daughterboard
cost
$400. The camera plus external video floppy drive package was $5,900
for
the Mac; $6,650 for Next; $6,350 for Microchannel computers; and $6,250
for AT-bus PCs.
http://global.canon/ja/c-museum/product/svc448.html
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Canon_RC-560_img_0830.jpg


![]()
![]()
CANON ION
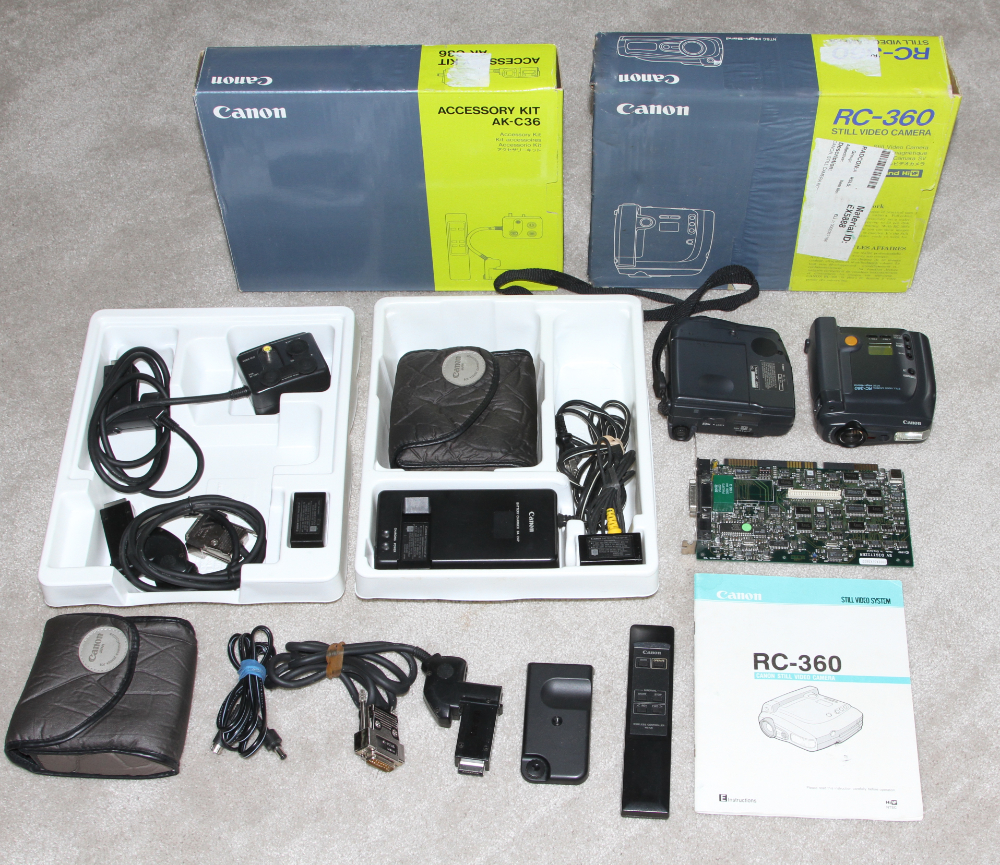
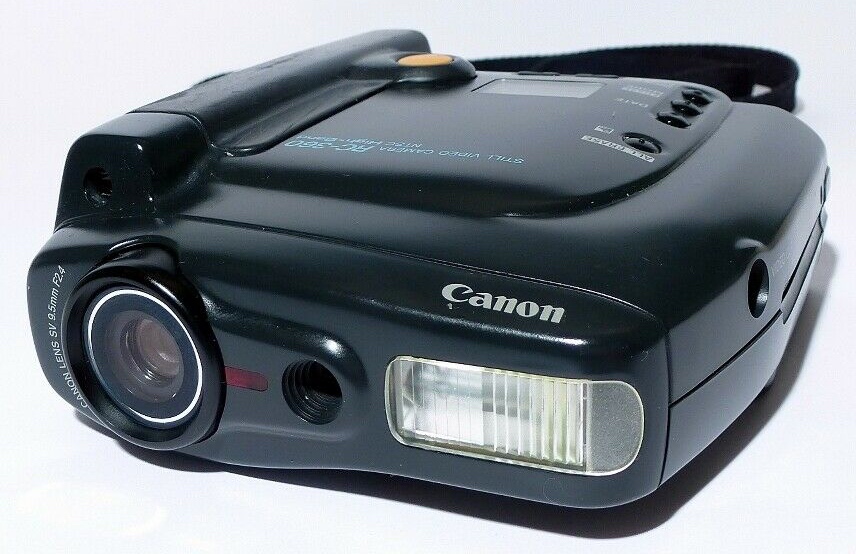
RC-360 AND SV-PV - 1992.
The RC-360 was a battery-powered still video camera with a 1/2-inch,
260,000 pixel CCD image sensor. Horizontal resolution of 380 TV
lines. The RC-360 could record up to 50 images on a miniature
floppy disk. All of the outputs were analog. Downloading
images into a computer required a digitizer such as the Canon SV-PC
digitizer board shown on the right of the left photo.
MSRP: $2,600 with digitizer. (Rare on U.S. eBay)
http://global.canon/en/c-museum/product/svc449.html
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/esvc/item/canon-rc360


![]()
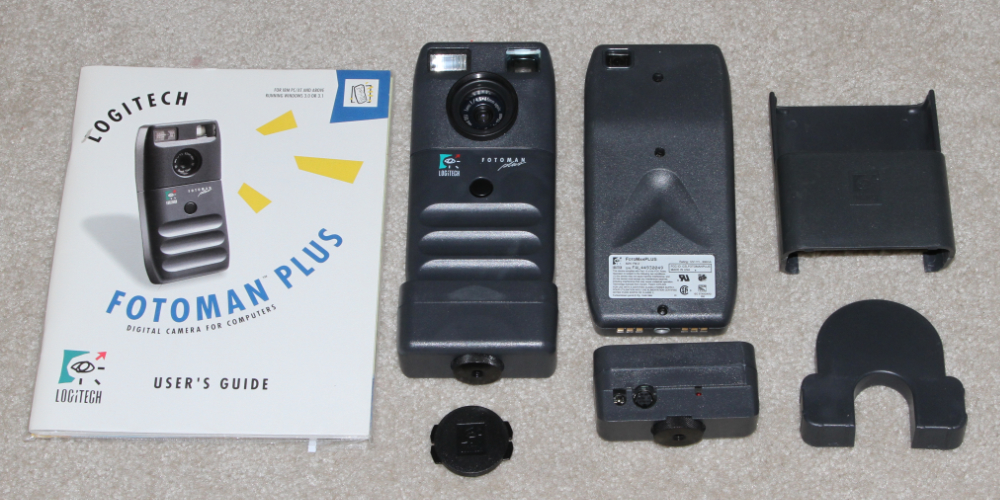
DYCAM
MODEL 3/3XL (LOGITECH FOTOMAN PLUS FM-2) - 1992. Fotoman Plus FM-2 version shown. Gray scale or 24
bit color when using an optional color filter system (contrary to what
you may read on some sites).
Lens 65 mm F/4.5. 495 x 366 pixel CCD. ASA 200.
Shutter 1/30 to 1/2000
second with flash, 1/20 to 1/2000 without flash, 1MB internal
storage.
Fixed-focus lens. MSRP
$695. The XL had 4MB storage and better battery. MSRP
$895. (Dycam versions Rare on U.S. eBay)
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Dycam
https://www.digicammuseum.de/kameras/detailansicht/kamera/Kamera/techdata/fotoman-plus/

FUJI
DS-H2
- 1992. 1/2-inch 390K pixel
CCD.
2X lens. Shutter 1/4 to 1/750 second. Memory
card stored up to 40 images. Built-in autoflash,
autofocus, and autoexposure control. Popular
Photography,
January 1993, p47. NOT MARKETED.
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/prototypes-rarities/item/fujix-ds-h2-prototype

FUJI HC-1000 IMAGE CAPTURE CAMERA - 1992. Also sold as the Crosfield Celsis 160. Three 900K pixel CCDs, 1280 x 960 pixel image. This camera was generally used for medical research purposes. Photo-Electronic Imaging, October 1992, page 50. MSRP $32,000 (approx $52,000 in 2011). Seybold Report on Publishing Systems, Vol 24 No. 21.
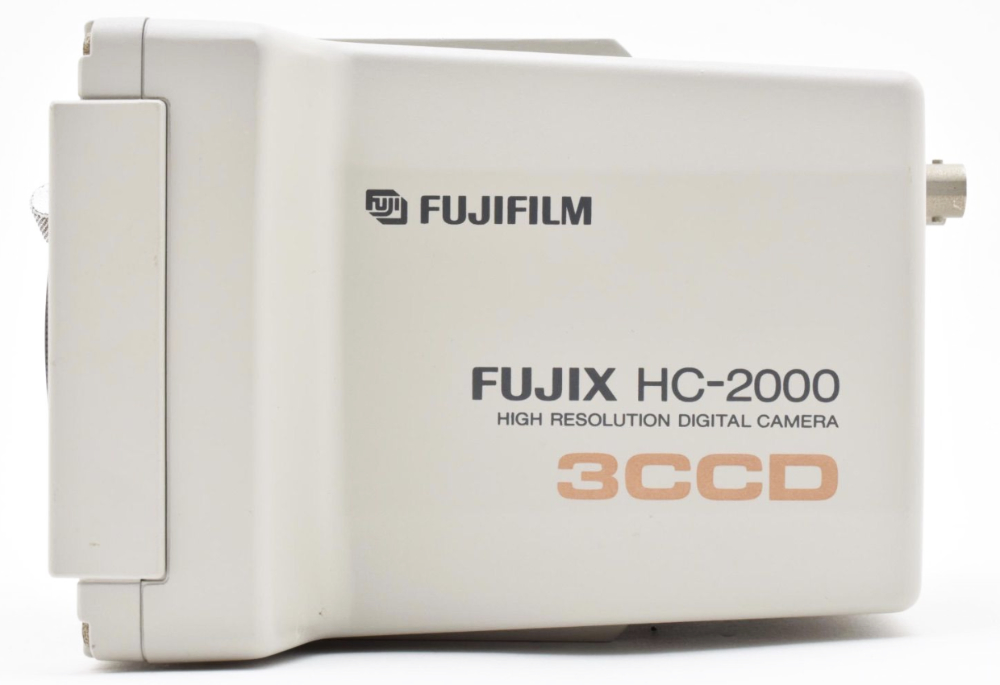



FUJI DC-X (HC-2000) IMAGE CAPTURE CAMERA - 1992. The DC-X (HC-2000) was a higher resolution version of the HC-1000. It used three CCD chips and was controlled from a small box with a separate control panel. A separate video output port enabled linking to a video display to check the image and focus.
Seybold Report on Publishing Systems, Vol 24 No. 21.
https://jp.mercari.com/shops/product/sKcuGGC3MPhg7UGUE3WWsc
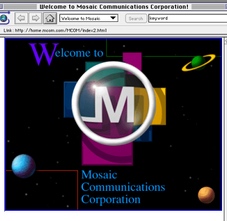

INTERNET PHOTO BROWSER - 1992. The National Center for Supercomputing Applications released Mosaic, the first browser enabling users to view photographs over the web. The National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA), is a unit of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
http://en.wikipedi.org/wiki/Mosaic_%28web_browser%




![]()
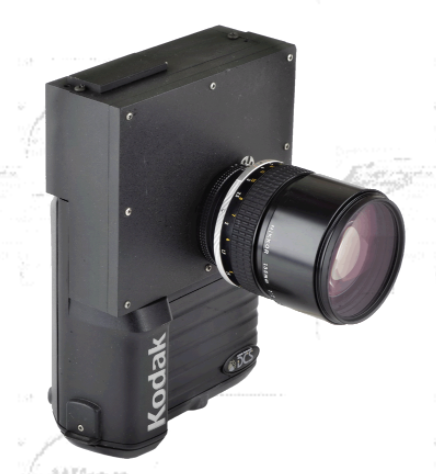
KODAK
DCS 200 - 1992.
The DCS 200 was the first digital camera that neatly integrated all its
essential components into one, permanently attached digital back.
The DCS 200
had
a built-in hard drive for image recording. On sale from 1992 to
1994,
it was based on the Nikon N8008s. There were five variants of the
DCS200: DCS 200 ci (color and integrated hard disk), DCS 200 c (color
without
internal hard disk), DCS 200 mi (black and white and integrated hard
disk),
DCS 200 m (black and white without internal hard disk) and the
'Wheelcam'
(color by a triple green red and blue exposures). Resolution with
the Kodak DCS 200 Digital camera was 1.54 million pixels, providing
four
times the resolution of still-video cameras at that time. Kodak's fully
digital systems used a Nikon body and optics to capture the image. The
image was then transferred to a CCD that converted the image directly
into
digital information. The CCD in the Kodak DCS camera system only used a
small portion of the angle of view compared to conventional cameras;
for
example, a 28mm lens on the Kodak DCS Digital Camera was equivalent to
an 80mm lens on a 35mm camera. The exposure index (EI) of the DCS
camera equated to 50 to 400 IS0 for color images and 100 to 800 IS0 for
black-and-white images . Kodak also made a special version of the
DSC 200 called the High Speed Target Camera for use in parks to take
photographs of visitors while they are on park rides. MSRP $9,995.
https://petapixel.com/kodak-dcs-history/
http://apphotnum.free.fr/N2BE10.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kodak_DCS



http://apphotnum.free.fr/N2BE10.html
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/cameras/item/dcs-200-hs


![]()
LOGITECH
Fotoman Plus (See Dycam Model 3 above) - 1992. 24
bit color (when using an optional color filter system) or gray
scale.
495 x 366 pixel CCD. ASA 200. Shutter 1/30 to 1/2000
second.
Fixed-focus lens. Internal storage up to 32 photos. MSRP
$695.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Logitech
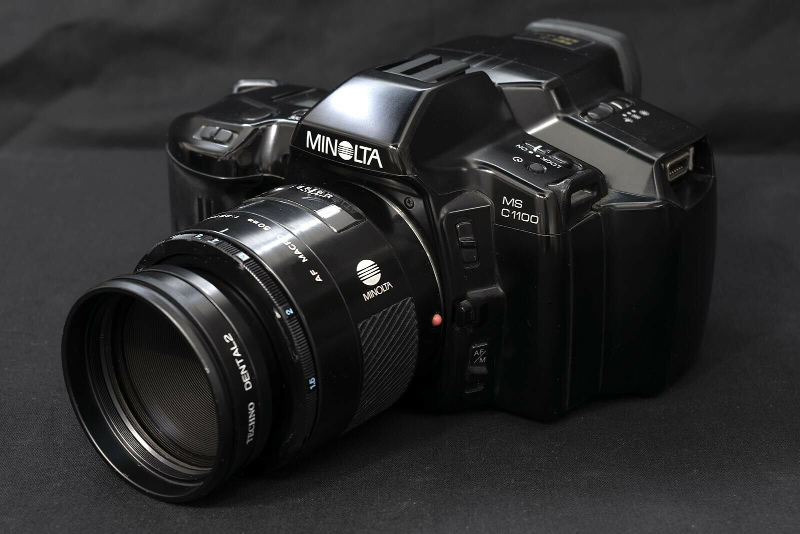

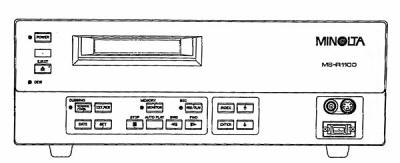
MINOLTA MS-C 1100 - 1992.
1/2 inch CCD, 360K pixels. ISO 100-200. Shutter 1/2 sec -
1/2000 sec and bulb. Required the use of Minolta DAT recorder MS-R 1100
as the camera had no independent recording ability. 12,000DM in
Germany. Not sold in U.S. Photo-Electronic Imaging, October 1992, page
50. MSRP $3,000.
http://www.mhohner.de/sony-minolta/onebody/ms-c1100
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Template:Minolta_AF_mount_DSLRs
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Minolta_Dynax_SPxi
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/cameras/item/minolta-ms-c1100


PCMCIA ATA (PC) Cards, Type II - 1992.
SanDisk launched its PCMCIA card in October 1992. The company was the
first to introduce a writeable Flash RAM card for the HP 95LX
(the first MS-DOS pocket computer). These cards conformed to a
supplemental PCMCIA-ATA standard that allowed them to appear as more
conventional IDE hard drives to the 95LX or a PC.
https://madpcb.com/glossary/pc-card/
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/memorycards
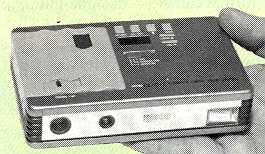

RICOH
DC-10 - 1992. Prototype memory
card camera. Popular Photography, May 1992, p52. NOT MARKETED.
X&ved=0ahUKEwj3yIWLv-XYAhUOUa0KHSQVA7AQ6AEIUTAK#v=onepage&q=RICOH%20%2B%20%22DC-10%22&f=false



![]()
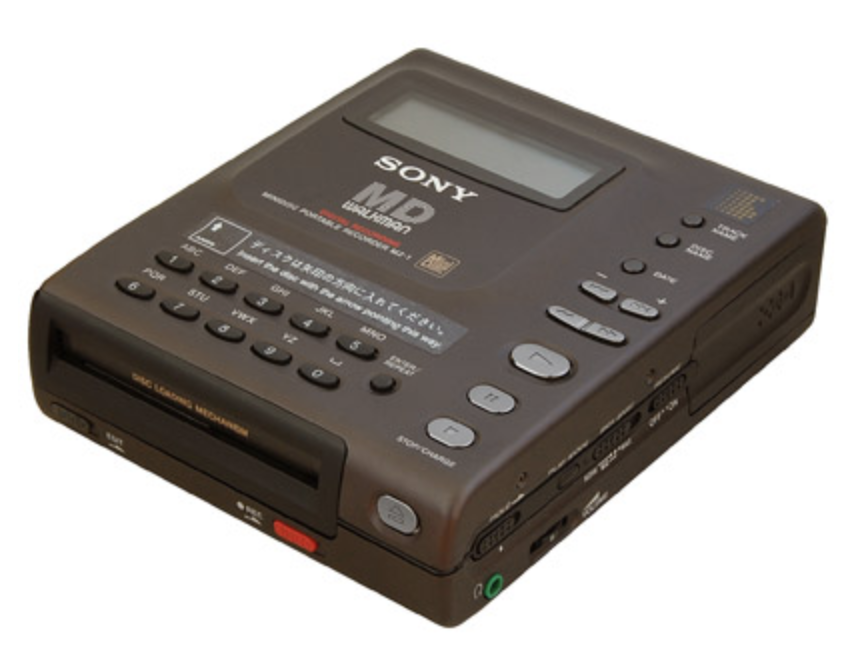
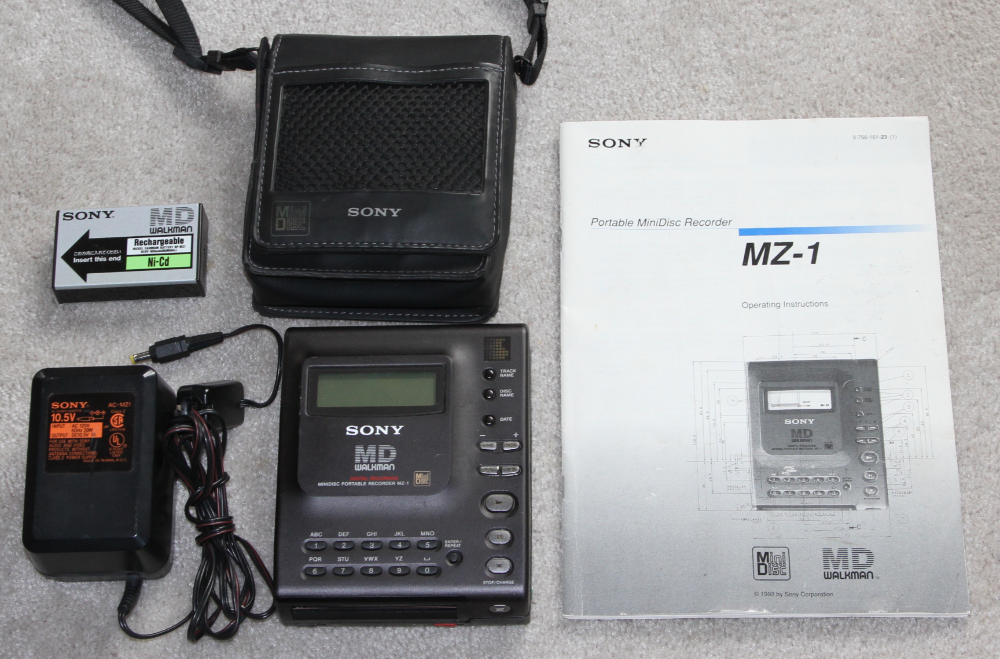
SONY MZ-1 - 1992.
In 1992, Sony marketed the first MD (MiniDisc) portable player.
The MZ-1 could record for up to 74 minutes, although 80 minute discs
would appear later. Recordings could be made from a microphone, an
analogue line-level source and from a digital source via an optical
cable. Once made, recordings could be divided, combined, deleted and
named. The MZ-1 used a lossy auto data reduction scheme called
ATRAC (Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding). Musicians liked
MiniDiscs because they were small, digital, portable and recordable, so
you could easily record, copy and carry demos in that format. MP3
players basically made the MZ-1 obsolete and in 2013 Sony discontinued
sale of the MZ-1. MSRP $750.
https://walkmancentral.com/products/mz-1
https://www.minidisc.wiki/equipment/sony/portable/mz-1
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WzQlKdjCHak


![]()
SONY
ProMavica MVC-7000 - 1992.
Professional SLR, 3 CCD chip still video camera. The MVC-7000
accepted
lenses designed for Nikon or Canon bayonet mounts. It had
through-the-lens
(TTL) viewing, a hot shoe, choice of center weighted or spot metering,
and variable ISO. An 8mm to 48mm zoom lens was
standard. MSRP $9,350.
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/esvc/item/sony-promavica-mvc-7000-1992
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sony_Mavica

![]()
SONY MVR-5600 - 1992.
Still video recorder that would be used to record and playback images
taken with the MVC-7000 or other still video cameras. As of June
2018, various models of Sony MVR still video recorders appear
frequently on eBay, usually in excellent condition.
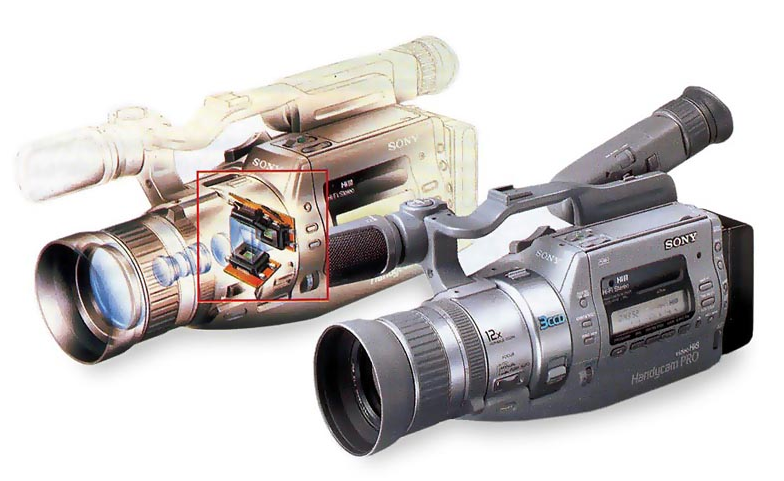

SONY CCD-VX1 - 1992. World's first 8mm video camera with three CCDs, one for each primary color.
1992